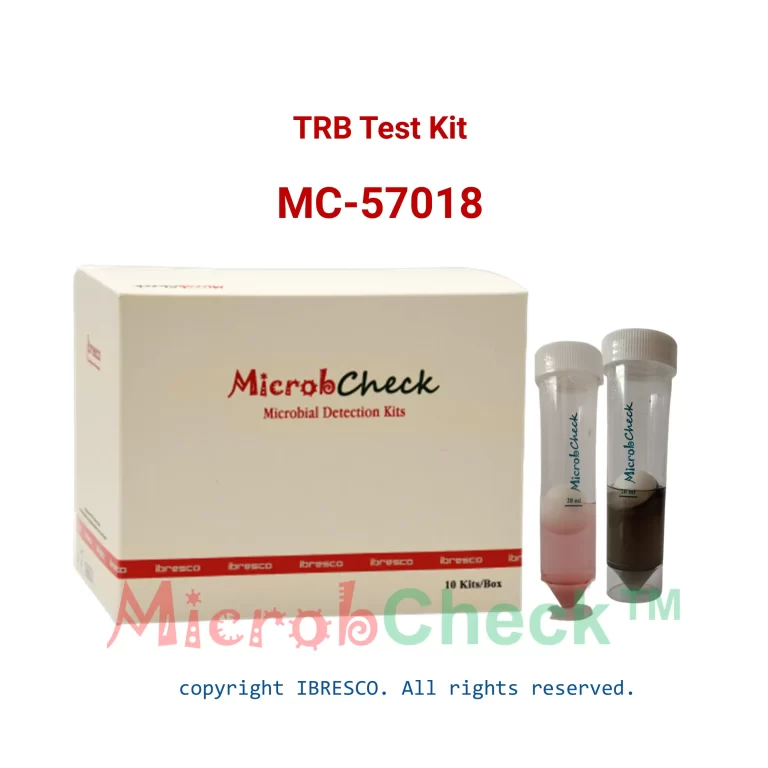
توضیحات
The corrosion caused in metals that are submerged in seawater leads to significant economic costs. It has been observed that the presence of thiosulfate increases the likelihood of biological corrosion in many oilfield facilities and similar installations. The activity of thiosulfate-reducing bacteria has also been repeatedly linked to anaerobic corrosion in complex biofilms. This microbial population affects iron by producing hydrogen sulfide gas. Thiosulfate-reducing bacteria cause the formation of iron sulfide on metal surfaces by using hydrogen. The bad smell of hydrogen sulfide, as well as the corrosion of metals and concrete caused by the growth of thiosulfate-reducing bacteria. Therefore, regular identification of these microorganisms is essential for controlling and preventing damage caused by their growth.
results interpretation
results interpretation
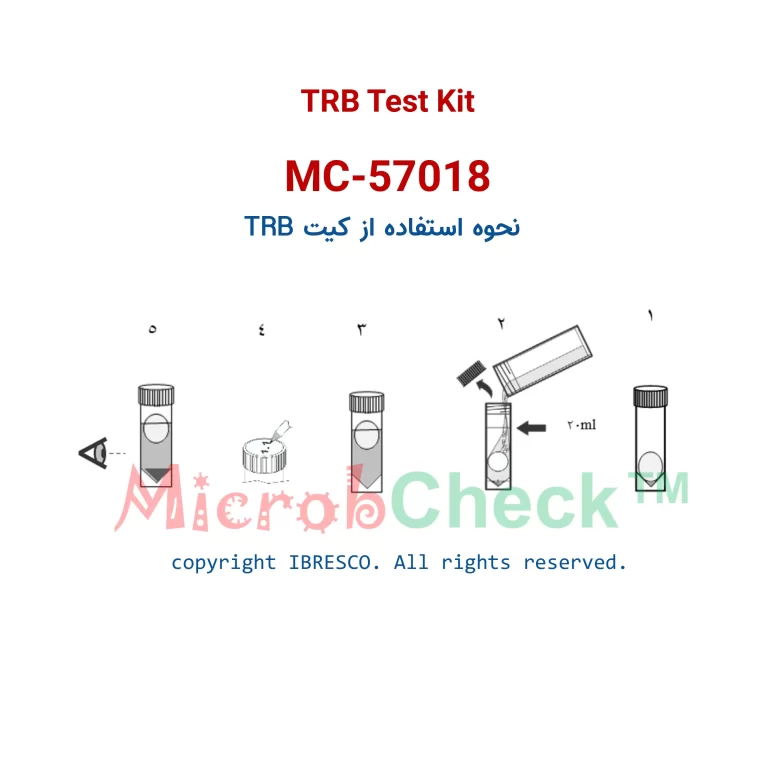
Presence/Absence Test
If there are thiosulfate-reducing bacteria present in the sample, after incubation, a black, muddy ring will form around the tube or muddy sediment will form at the bottom of the falcon tube. If these bacteria are absent, there will be no black coloration in the solution.
Bacterial Count Estimation:
If the test result is positive, you can estimate the bacterial population and the extent of their invasion according to the tables below. A faster reaction occurs when there is a higher bacterial population.
Note: The presence of more than 20 ppm of hydrogen sulfide gas in the sample will cause a false positive result. To remove hydrogen gas from the sample, pour 30 ml of the sample into a tube, close it, and shake it for 10 seconds. Then let the tube stand for 20 seconds. After that, you can use this sample for testing.